Topics
History of the Computer
- The computer's evolution is contributed by various mathematicians and scientists
von Neumann Architecture
- von Neumann Architecture is the architecture of modern computers nowadays
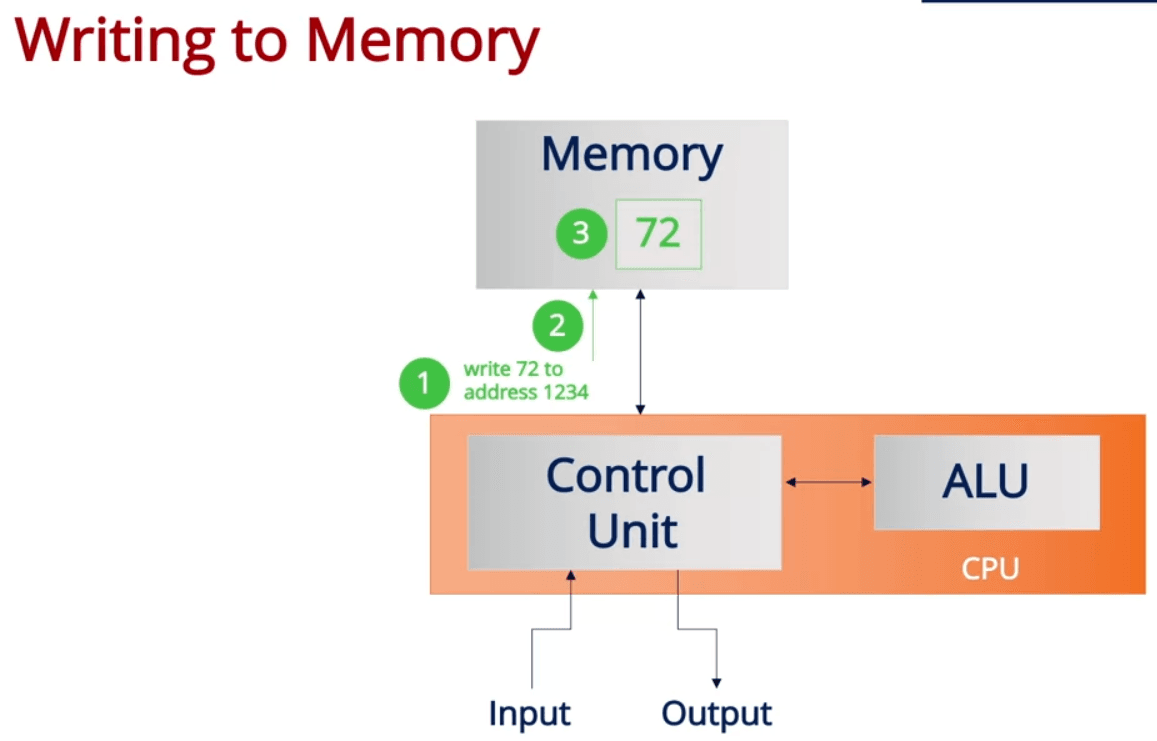
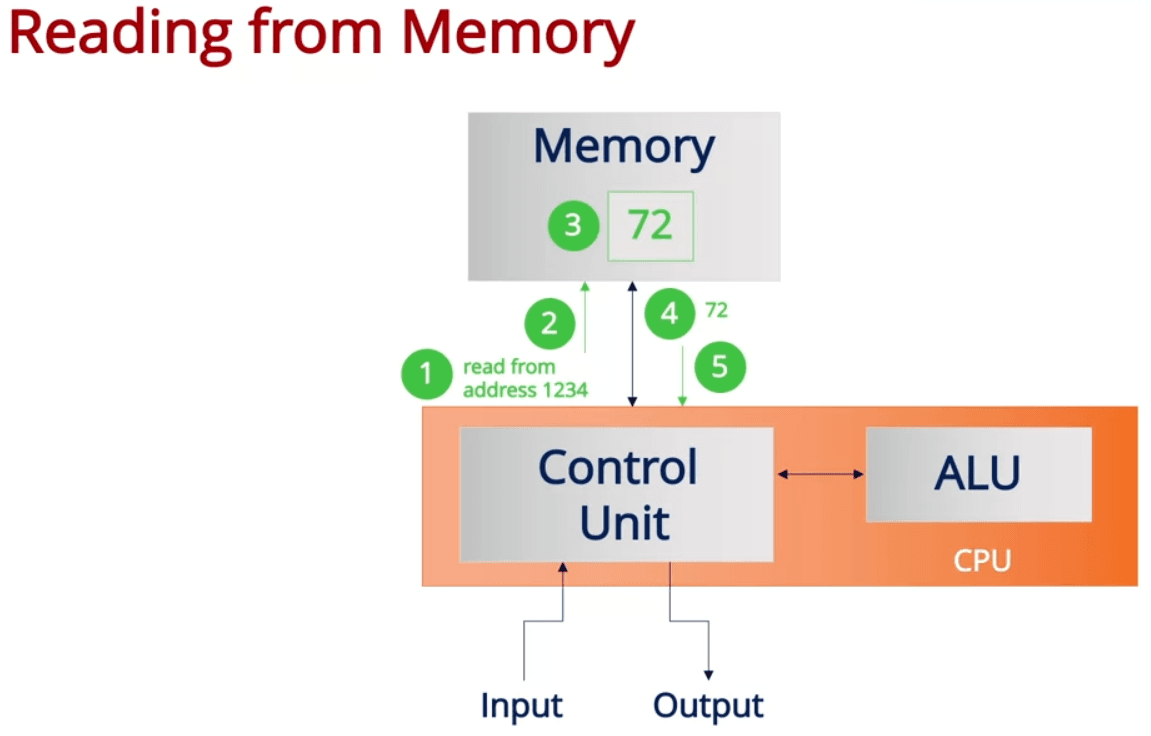
- When using computational thinking, it is important to know what the computer's capability
- Central Processing Unit contains Control unit and Arithmetic Logic unit
von Neumann Architecture Data
- Computer operator used to manipulate the data of each address physically
- From electric connector to punch card, and even mini computers
- Modern computers have so many addresses that it is impossible to manually do it anymore, so we use variables to represent the address of values
- The lecture used a good analogy, which is we will not tell the cab driver to go to what address, instead, we will tell them the building's name so they will bring us there
- It is also true for how modern computers works, by inputting the variable name, CPU will decode the input to actual address and execute the command on memory
- Collection
- A series of data with order (List in Python)
- Object
- A set of data with nested data (Dictionary in Python)
- Assembly Language
- Remember you have an OUTPUT slot, after doing certain operations such as ADD, SUB, it is your freedom whether to WRITE it
- Some CPU will have many registers, we only used two for simplicity's sake in the exercises
von Neumann Architecture Control Flow
- Program instructions are executed in sequential order (typically)
- Conditional Execution
- if else in programming language
- Loop
Pseudocode
- Human readable, otherwise for computer
- No standard syntax, but there are some conventions
- Use
<-to assign value to variables
Remarks
- This was a worthwhile week because I have never learned how assembly code works
- In the assignment, I learned how to write simplified assembly code and how CPU works
- Apparently, there are more about assembly code (opens in a new tab) and the process that is involved before it is turned into machine code, such as Opcode & Bytecode (opens in a new tab)