Topics
Finding the Largest Value
- Different from human, traditional computer can only read a binary data at a time
- Which makes it only can add data or compare data at the same time
- It does not matter whether the value you are looking for is the minimum value or maximum value
- Similar algorithm could be applied in different tasks
Linear Search
- Search one by one and find matches
- The lecture used an example of searching for a specific time slot of a day from a few days
- There should be a more effective way to do it (e.g. Binary Search?)
Algorithmic Complexity
- Time complexity is the maximum number of steps we need to take when applying certain algorithm
Binary Search
- Can only apply on sorted items
- Cut half of the operations
- The algorithm is to select the middle item of the list, if it is not the target, compare it with the target, select first or second half depending on the result of comparison
- If the list is unsorted, it will takes N log N to sort the list
Brute Force Algorithm
- Trying out all the possibilities
- There are problems we have no choice but to use brute force, which might involve the following complexities
- Exponential complexity
- Factorial complexity
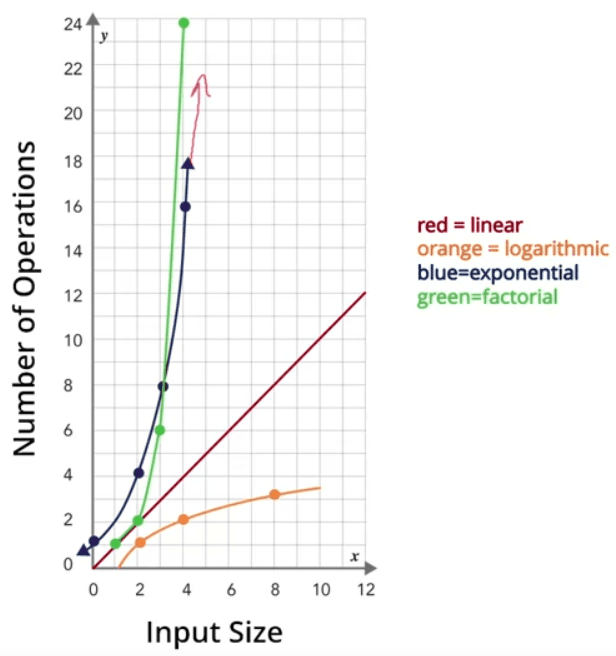
- Brute Force guarantee the most optimal solution since you would have tried all possibilities
Greedy Algorithms
- Greedy provide a good solution at first sight, without much effort
- However, It does not guarantee the optimal solution
- Example 1.
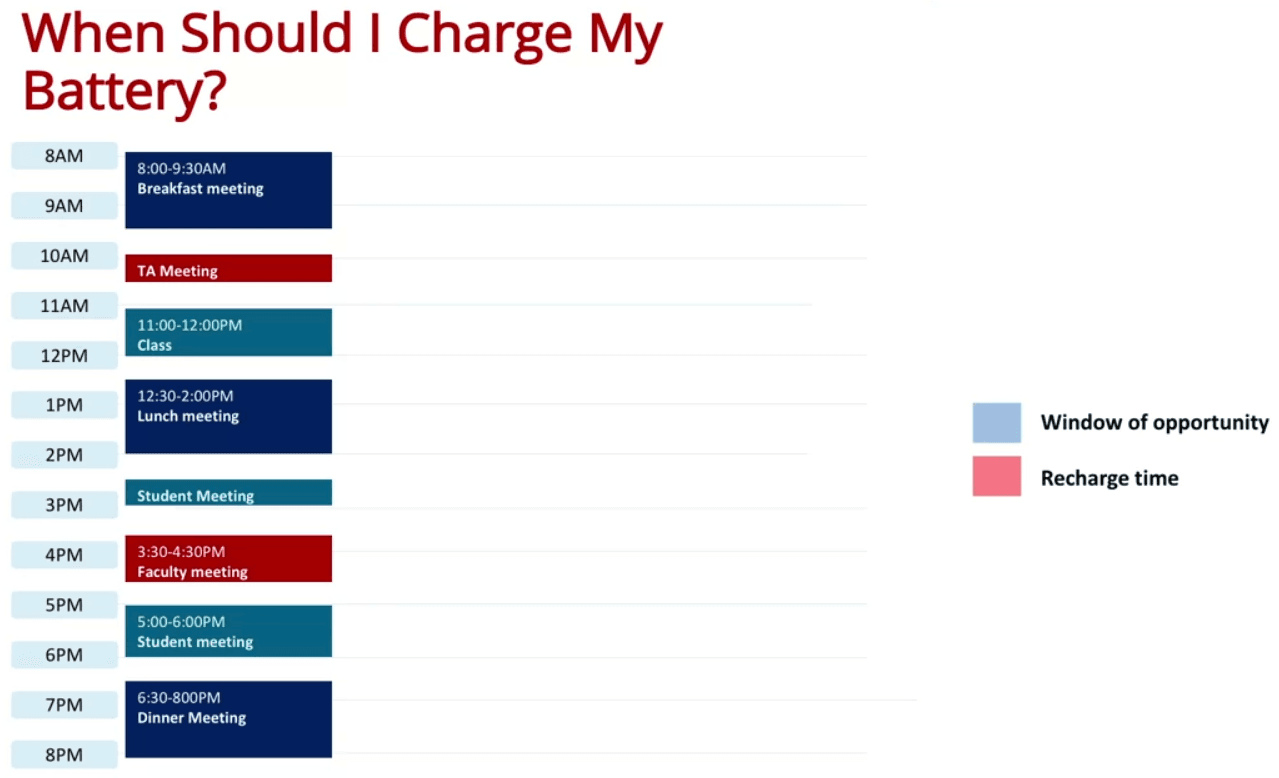
- Try to minimize the number of charging, while providing enough power for the work days
- Each charging will allow the laptop to work for three hours
- Using brute force, we would have tried all combinations, such as charging in every break
- We will also come up come useless combinations, such as not charging at all (They are still part of the result from brute force!)
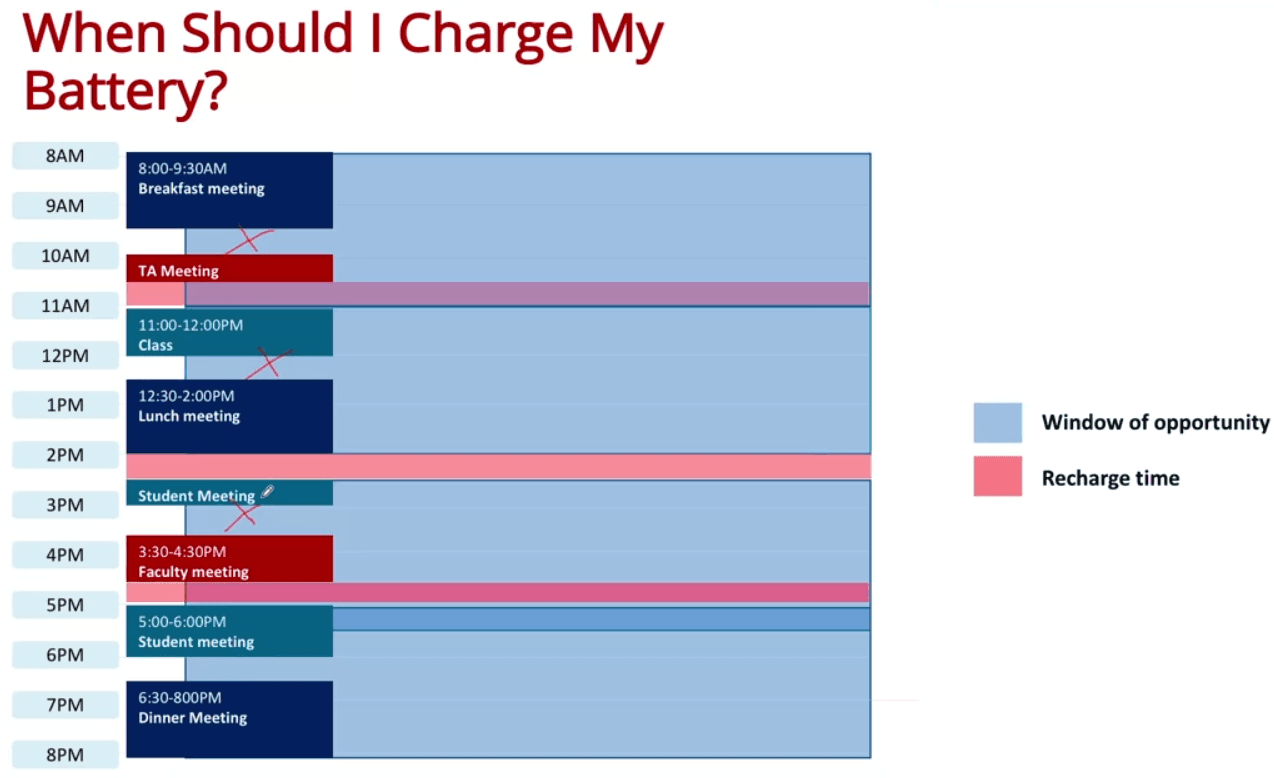
- But using Greedy, we will approach the problem with "Try to charge for minimal times and maximize each charging"
- Example 2.
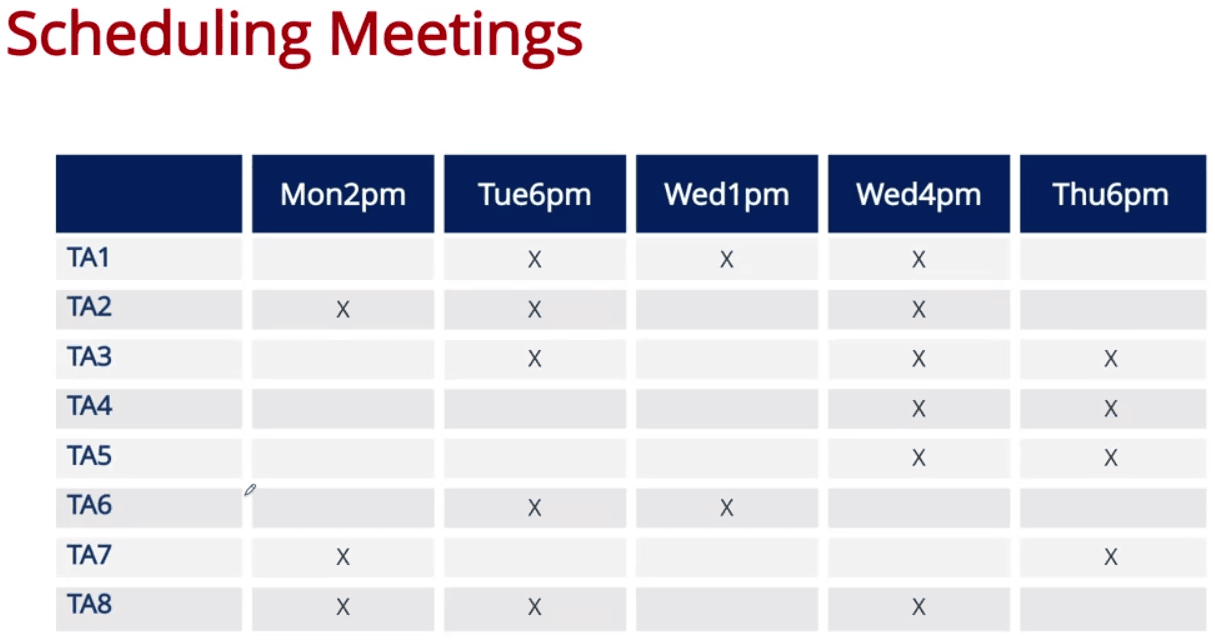
- Try to minimize the number of days with appointments while meeting all TA in a week
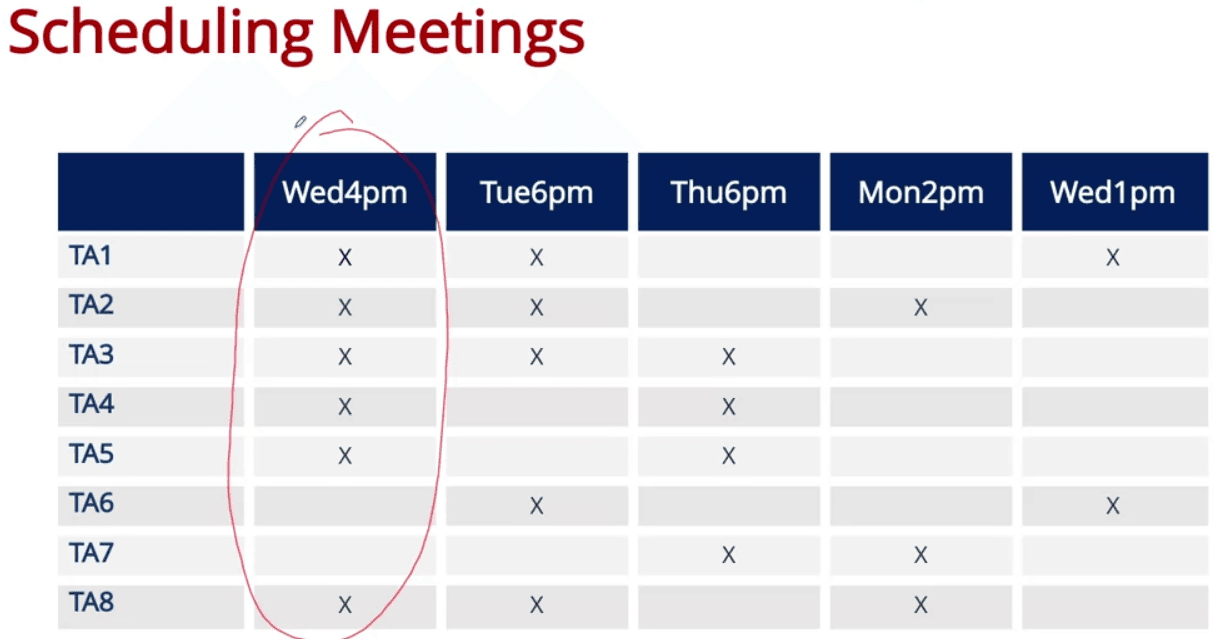
- We sort the time slots with largest number of available TAs, and found the solution with Wed 4pm, Tue 6pm & Thu 6pm
- However, this example also showed the fact that Greedy is not always the optimal, as we can just choose Tue 6pm & Thu 6pm
- Use cases:
- Use greedy if we don't have computer to do brute force for us
- Use greedy if we have large input and don't want to wait for long time
Case Studies
- Quadratic Complexity
- Loop nested inside a loop, making the increase of complexity goes up quadratically
- O(n^2)
- Linear Complexity
- Only 1 loop
- O(n)
- The example that uses trained dog's attributes to determine whether the dog could become rescue dog used K Nearest Neighbor Method (opens in a new tab)
Remarks
- I can relate to the Scheduling Meetings example in Greedy Algorithm much, since I am facing the same situation when working on the Voting Scheduler (opens in a new tab) project
- Although I haven't proceeded to the result part for host to select the best date, implementing such feature will make my APP lot useful!